Sustainable Musical Instrument Manufacturing
At Yamaha, living in harmony with people and the planet is at the heart of everything we do. All over the world, Yamaha Group companies strive to make positive differences in the environment, as well as in local communities, so that people of all ages can continue following their musical passions for generations to come.

Afforestation in Tanzania in cooperation with local communities
The bodies of clarinets, oboes and piccolos are made from the black, solid lumber Grenadilla (African Blackwood). The country of origin is the United Republic of Tanzania in Africa.
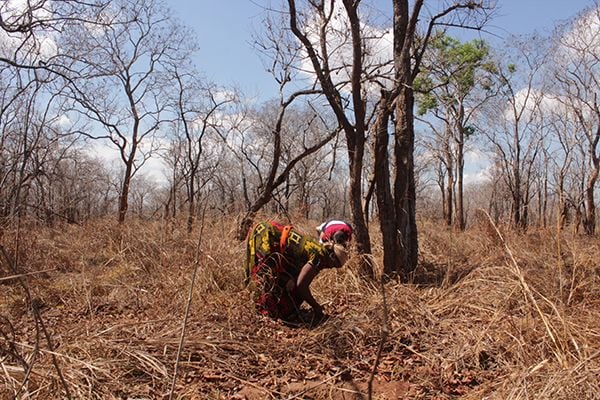

Grenadilla is indispensable for manufacturing of musical instruments. However, this wood is at risk, becoming increasingly precious and rare.
Therefore, together with Tanzanian NGOs and residents, Yamaha is promoting afforestation activities. So far, we have been able to plant about 7,400 trees in four years.
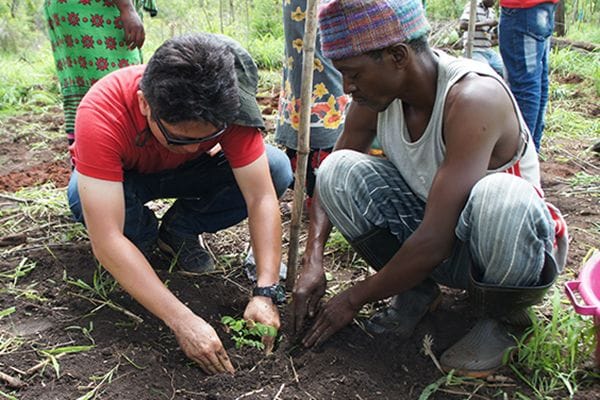

It takes more than 100 years for trees to grow to the right size before they can be crafted into musical instruments. To ensure that forests and musical instruments will still be here 100 years from now, Yamaha is working with its partners – the villagers – to address any potential issues.
In this initiative, 95% of turnover from logging and sales are village revenues. Thanks to this structure, new elementary school and village offices have been established, and new beds and mattresses have been brought to clinics. In addition, we are enriching the lives of women by providing them with hospital expenses and allowances so that their children can continue attending school.
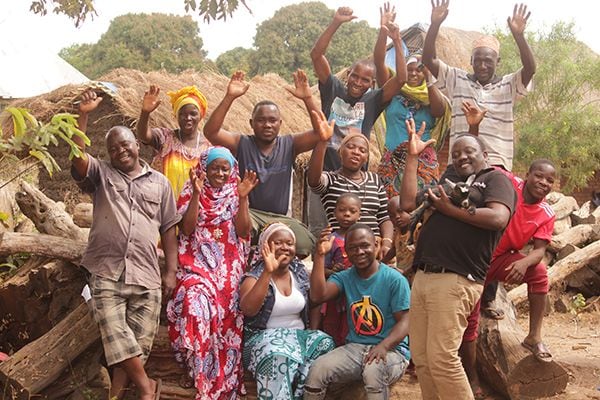

Other promises Yamaha has made:
- Procure timber from certified forests
- Use legally cut and traded lumber with clear supply sources
- Confirm that there are no human rights violation in the place of origin
- Refuse to use genetically modified tree species
- Use existing resources as efficiently and carefully as possible, and continue basic research on this very topic
World’s First Mass Production of Musical Instruments
Using Lead-Free Solder
One of the many processes performed by craftsmen in wind instrument factories is soldering together fine metal parts.

Generally, lead is used for soldering. However, lead may have a negative impact on human health. It could also contaminate the environment.
To manufacture musical instruments that are friendly to humans and the environment, Yamaha has conducted a number of studies. As a result, for the first time in history, we’ve succeeded in mass-producing wind instruments using lead-free solder.
Currently, all the wind instruments* shipped from Yamaha factories use this lead-free solder.
*Excluding gold flutes
Reduction of formaldehydrocarbons
Not only wind instruments but also percussion instruments are being implemented. To reduce formaldehyde use, Yamaha has improved equipment, adhesives, and processing conditions at its percussion and winds factories.
Efforts to Protect Environment at Yamaha Wind Instrument Factories
Yamaha manufactures wind instruments at factories in Shizuoka Prefecture, Japan, China and Indonesia.
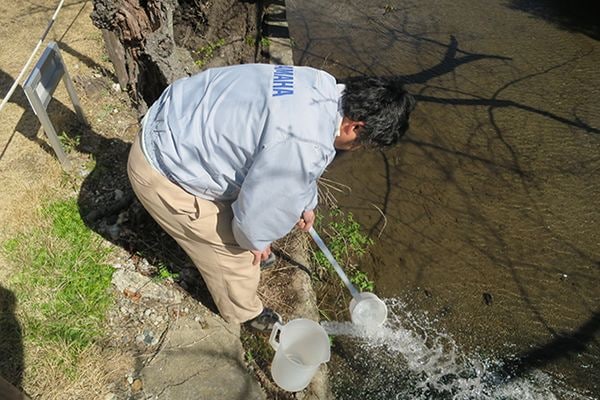
When making wind instruments at a factory, a large amount of water is required to cooling the heated and processed parts, cover the metal membrane on the surface (plating), and clean the musical instrument. As a result, a large amount of waste liquid is generated.
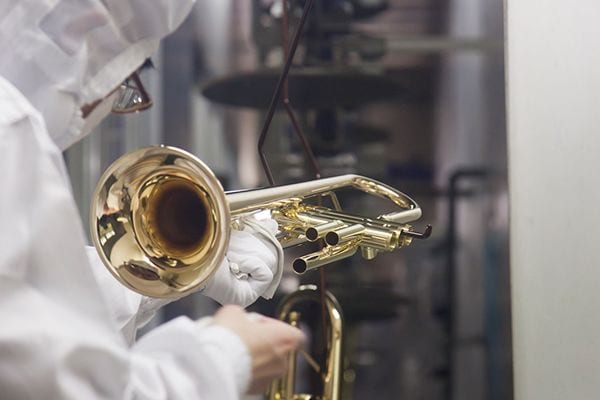

To conserve water, Yamaha has been working since 1970 on the use of recycled water and measures to prevent leakage of harmful substance. For example, we are continuing to conduct periodic surveys to check whether plant wastewater has had an impact on water quality and the environment so as not to have a negative impact on rivers or the sea. Currently, we have confirmed that there is little impact on ecosystem.