QoS
Priority Queuing
You can use priority control to send packets with higher priorities from the router first. The router can identify packets by their IP addresses, port numbers, etc., and prioritize the transmission of data that it is important to send in real time and data whose loss you want to minimize as much as possible.
Shaping
You can use bandwidth control to control the amount of traffic for each type of data sent from the router.
The router can identify packets by their IP addresses, port numbers, etc., and transmit the packets such that each type of traffic remains below its specified limit.
This enables you to use multiple services in a network environment while minimizing the influence that the services have on each other.
DTC (Dynamic Traffic Control) Queing
Dynamic traffic control is an expanded version of bandwidth control. When the traffic on a line is heavy, communication is performed so as to protect the specified bandwidths, but when the traffic on a line is light, communication is allowed to exceed the specified bandwidths.
Dynamic traffic control enables you to use a line's bandwidth effectively.
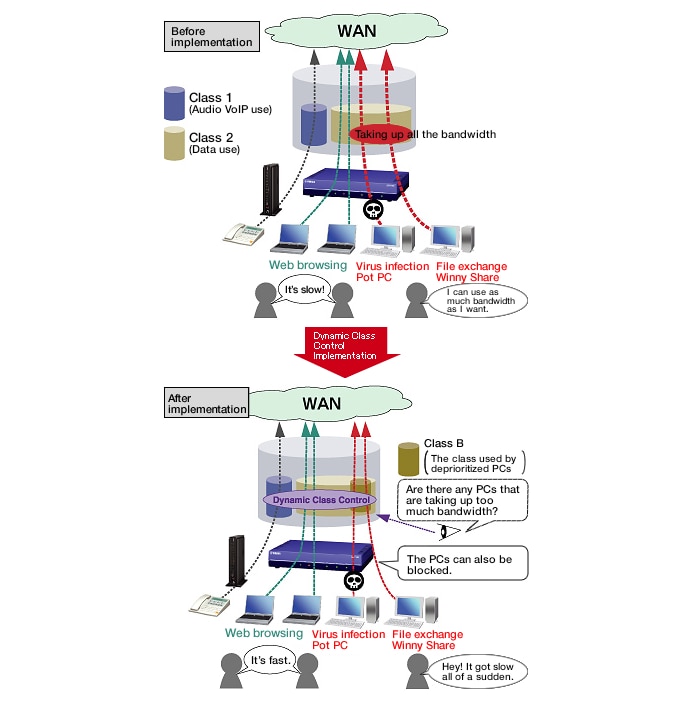
Dynamic Class Control
Dynamic class control is an expanded version of bandwidth control. You can use dynamic class control to identify communication that is taking up line bandwidth and dynamically change the bandwidth that the communication can use.
When a terminal is infected with a virus and is generating massive levels of traffic or when a terminal is using filesharing software and taking up too much bandwidth, dynamic class control can be used to dynamically reduce the bandwidth that is available to the terminal and reduce its impact on other terminals.
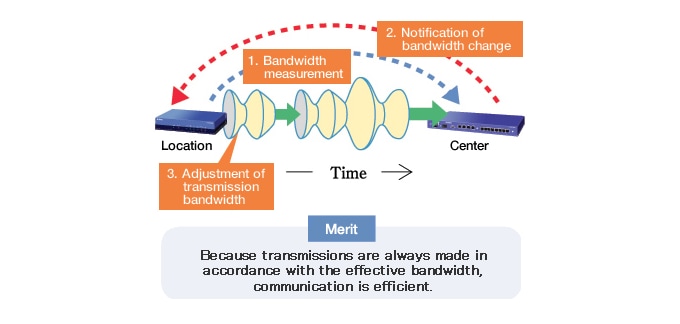
Bandwidth detection
Bandwidth detection enables more accurate QoS control for changing bandwidths
In bandwidth detection, routers that are connected over the Internet send and receive bandwidth detection packets to measure the effective bandwidth at different points in time.
You can use the effective bandwidth as a guide for performing efficient communication by linking QoS functions to the measured effective bandwidth.
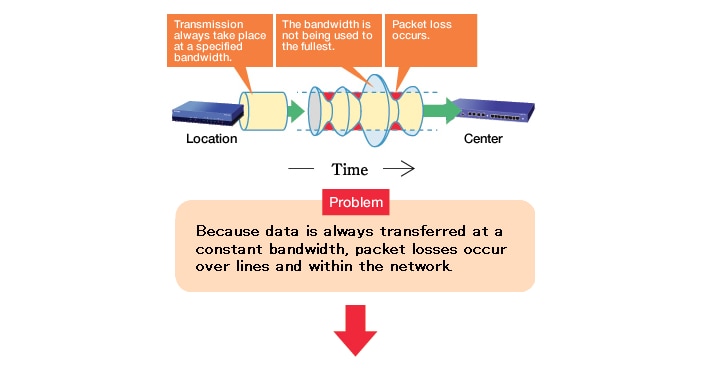
Problems with conventional QoS configuration
The transfer bandwidth between the center and the other locations is set using intuition.
QoS using bandwidth detection
The effective bandwidth between the center and the other locations is measured regularly, and the results affect the transfer bandwidth.
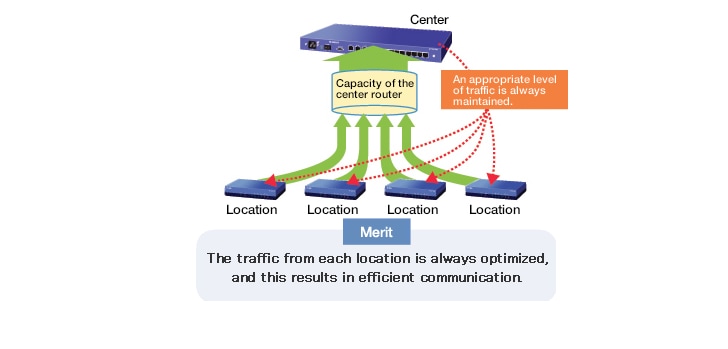
Load notification
More reliable reception is possible, even during instances of concentrated communication traffic.
When a center location connected to multiple other locations is subjected to a high load, it can use load notification to send a control packet to the routers at the other locations that instructs the routers to reduce their traffic levels, and the routers that receive the control packets will reduce their traffic levels in accordance with the load condition of the center location.
By maintaining the stability of the center location, where the load is concentrated, you can create an environment that supplies stable service.
Problems with conventional traffic concentration
The sum of the traffic from the other locations exceeds the capacity of the center router.
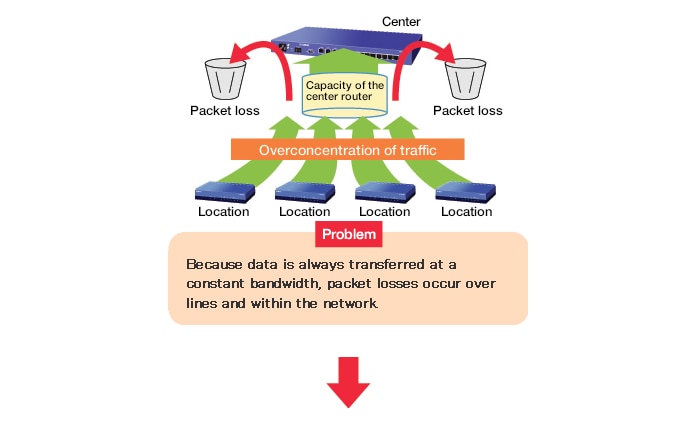
Load notification results in appropriate traffic control.
The traffic from the other locations is limited according to the capacity of the center router.